Minimally Invasive Surgery


Immediately Call Medical Health Care
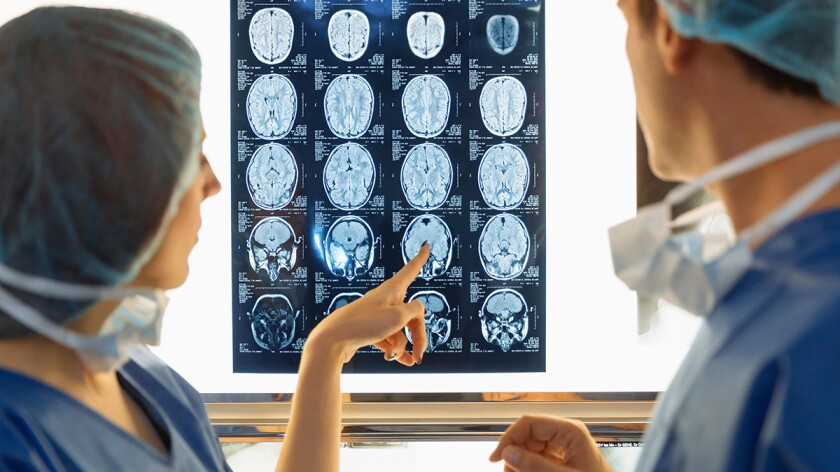
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Minimally invasive surgery uses new technology and techniques to access your organs through small portals, rather than large incisions. Surgeons today can complete many common operations using minimally invasive methods. Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) is an approach to surgery that minimizes cutting through your skin and tissues. Surgeons use MIS techniques and technology to cause as little trauma as possible during your procedure. Smaller cuts reduce your potential for pain, complications and recovery time. Healthcare providers perform many common procedures today using minimally invasive surgery techniques.
Keyhole Surgery
Most minimally invasive surgery procedures involve the use of small, “keyhole” incisions to serve as ports for special instruments during your surgery. Depending on the location, these incisions are usually a half-inch long or less. One port provides access for an endoscope, a narrow tube with a lighted camera at the end that projects images to a screen. Surgeons operate through the other ports with long, narrow instruments.
There are different types of endoscopes for different body parts, and sometimes they go by specific names. For example, a laparoscope goes into your abdominal cavity, a thoracoscope goes into your chest cavity and an arthroscope goes into your joints. Surgery using these scopes may be called laparoscopic surgery, thoracoscopic surgery or arthroscopic surgery. These are a few types of minimally invasive surgery.
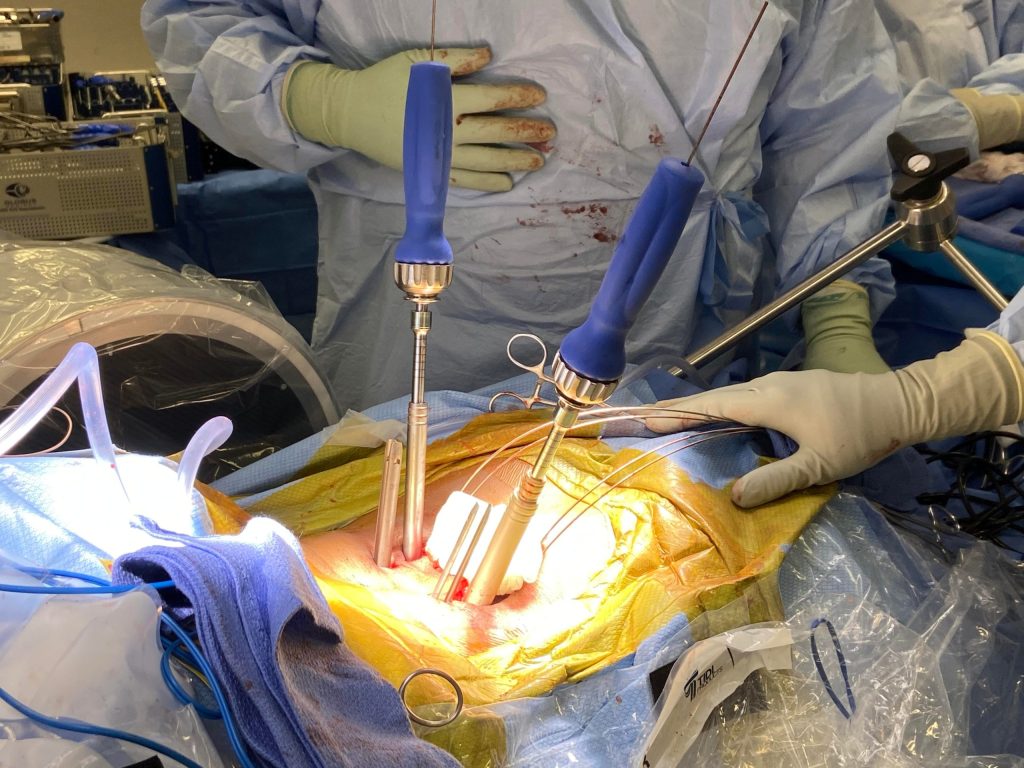
Endovascular Surgery
Robotic Surgery
Endovascular surgery involves threading a tiny catheter through a blood vessel and operating through it. It takes only one tiny incision to access the blood vessel. Often, endovascular surgeons can puncture the skin with a needle rather than cutting it. This minimizes bleeding. Surgeons thread the catheter over a guidewire, then remove the wire and pass surgical instruments through the catheter to operate.
An advanced form of minimally invasive surgery uses robotic arms to operate through the small incisions. This is called robotic surgery. A specially trained surgeon operates the robot arms from a console within the operating room. Robotics allow for greater precision and control in smaller areas. Most robotic surgery procedures use several ports, but sometimes single-port surgery is possible.
What are some examples of minimally invasive surgery procedures?
- Minimally invasive urological surgery: Kidney removal (nephrectomy), prostate removal (prostatectomy) or pelvic organ prolapse repair (sacrocolpopexy).
- Minimally invasive spine surgery: Spinal fusion, tumor removal and to treat spinal stenosis.
- Minimally invasive heart surgery: Atrial septal defect repair and mitral valve repair.
- Arthroscopy: Shoulder arthroscopy to treat rotator cuff tears, ankle arthroscopy to treat ankle pain or hip arthroscopy to repair minor hip damage.
- Video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS): Thoracoscopy-guided procedures to treat cancer in your chest cavity, or to repair pectus excavatum (Nuss procedure).
- Laparoscopic surgery: Gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy), appendix removal (appendectomy) adrenal removal (adrenalectomy) and hernia repair.
- Endovascular surgery: Angioplasty, atherectomy, embolization and stenting.
- Functional endoscopic sinus surgery: Endoscopic sinus surgery for serious sinus conditions.
- Endoluminal surgery in your gastrointestinal tract: Tumor removal (endoscopic submucosal dissection or transanal endoscopic microsurgery) and sphincter myotomy.
- Epilepsy surgeries: Stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) and deep brain stimulation (DBS).
- Bariatric surgeries: Gastric sleeve surgery and gastric bypass surgery for weight loss.
Endoscopic Surgery
Finally, some endoscopes can go through an existing opening in your body, like your nose or mouth. Surgeons can operate through these endoscopes using long, narrow tools, without cutting through your skin at all. This is called “natural orifice” endoscopic surgery. “Endoluminal” procedures happen within the walls of your organ, while “transluminal” procedures cut through one of the walls of your organ.


